Ordinary Course Of Business
Ordinary Course Of Business - Learn the meaning and usage of the term ordinary course of business in merger and acquisitions contracts. A person that buys goods in good faith. When a party seeks to recover costs or damages from a transaction that was made impossible by a breach or tort, the courts use ordinary course of business calculations to ascertain how. Find out how this term affects. The usual transactions, customs and. Learn the legal definition and usage of the term ordinary course of business (ocb) in united states law. The phrase “ordinary course of business” is utilized in m&a agreements to require the target business to operate during the period between the signing and closing of an m&a transaction. Learn the meaning, examples and faqs of the legal term 'ordinary course of business', which describes the usual and expected activities of a company. A person that buys goods in good faith. The ordinary course of business refers to the standard practices and activities that a business engages in on a regular basis. The usual transactions, customs and. Find out how this term affects. Learn the meaning and usage of the term ordinary course of business in merger and acquisitions contracts. Ordinary course of business is a phrase used to determine the routinr record keeping and other procedures applied to the mainenance of something. In simple terms, it refers to the usual and. Learn the legal definition and usage of the term ordinary course of business (ocb) in united states law. Find out what activities are considered normal, consistent and customary for a. Grants and scholarshipsflexible classesmaster's degree programstransfer credits A person that buys goods in good faith. Conducting business in a consistent. It is often necessary for the bankruptcy courts to determine whether certain conduct is in the ordinary course of business. this issue may arise in several dif ferent contexts. A person that buys goods in good faith. This article focuses on the ordinary course of business (“ocb”) defense contained in section 547(c)(2) of the bankruptcy code, and the new value. Grants and scholarshipsflexible classesmaster's degree programstransfer credits Ordinary course of business, when applied to a transaction, means: Ordinary course of business is a legal term that has its roots in the uniform commercial code (ucc) as it pertains to commercial transactions. The usual transactions, customs and. This article focuses on the ordinary course of business (“ocb”) defense contained in section. Ordinary course of business is a phrase used to determine the routinr record keeping and other procedures applied to the mainenance of something. The usual transactions, customs and. Learn the meaning, examples and faqs of the legal term 'ordinary course of business', which describes the usual and expected activities of a company. The phrase “ordinary course of business” is utilized. A person that buys goods in good faith. The meaning of ordinary course of business is the usual manner and range of a business especially considered in relation to the amount, circumstances, and. It is often necessary for the bankruptcy courts to determine whether certain conduct is in the ordinary course of business. this issue may arise in several dif. (1) a transaction that is usual and customary in the business in question on terms that are not preferential; Ordinary course of business is a phrase used to determine the routinr record keeping and other procedures applied to the mainenance of something. Learn the legal definition and usage of the term ordinary course of business (ocb) in united states law.. Normal/ordinary course of business means all activities that are necessary, normal or incidental to the business of the company and are permitted by objects of the company including. When a party seeks to recover costs or damages from a transaction that was made impossible by a breach or tort, the courts use ordinary course of business calculations to ascertain how.. Ocb covers the usual transactions, customs and practices of a certain business and of a certain firm. Ordinary course of business, when applied to a transaction, means: The meaning of ordinary course of business is the usual manner and range of a business especially considered in relation to the amount, circumstances, and. Normal/ordinary course of business means all activities that. Ordinary course of business is a legal term that has its roots in the uniform commercial code (ucc) as it pertains to commercial transactions. A person that buys goods in good faith. The phrase “ordinary course of business” is utilized in m&a agreements to require the target business to operate during the period between the signing and closing of an. When a party seeks to recover costs or damages from a transaction that was made impossible by a breach or tort, the courts use ordinary course of business calculations to ascertain how. The meaning of ordinary course of business is the usual manner and range of a business especially considered in relation to the amount, circumstances, and. Learn the meaning,. It is often necessary for the bankruptcy courts to determine whether certain conduct is in the ordinary course of business. this issue may arise in several dif ferent contexts. A person that buys goods in good faith. Find out how this term affects. The meaning of ordinary course of business is the usual manner and range of a business especially. A person that buys goods in good faith. Learn the meaning, examples and faqs of the legal term 'ordinary course of business', which describes the usual and expected activities of a company. The ordinary course of business refers to the standard practices and activities that a business engages in on a regular basis. Find out what activities are considered normal, consistent and customary for a. The meaning of ordinary course of business is the usual manner and range of a business especially considered in relation to the amount, circumstances, and. Learn the meaning and usage of the term ordinary course of business in merger and acquisitions contracts. This article focuses on the ordinary course of business (“ocb”) defense contained in section 547(c)(2) of the bankruptcy code, and the new value defense contained in section 547(c)(4). (1) a transaction that is usual and customary in the business in question on terms that are not preferential; Conducting business in a consistent. Learn the legal definition and usage of the term ordinary course of business (ocb) in united states law. Understanding the “ordinary course of business” is crucial in legal contexts, as it evaluates whether actions align with standard industry practices. Ordinary course of business is a phrase used to determine the routinr record keeping and other procedures applied to the mainenance of something. Find out how this term affects. The phrase “ordinary course of business” is utilized in m&a agreements to require the target business to operate during the period between the signing and closing of an m&a transaction. A person that buys goods in good faith. Grants and scholarshipsflexible classesmaster's degree programstransfer creditsRELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS AND DEPOSITS ppt download
PPT Innovation, Technology, and Ordinary Course of Business
Meaning of ordinary course of business under Companies Act, 2013
Related Party Transactions ppt download
PPT Innovation, Technology, and Ordinary Course of Business
Ordinary Course Of Business Definition What Does Ordinary Course Of
Decoding “Ordinary Course of Business” in M&A Transactions
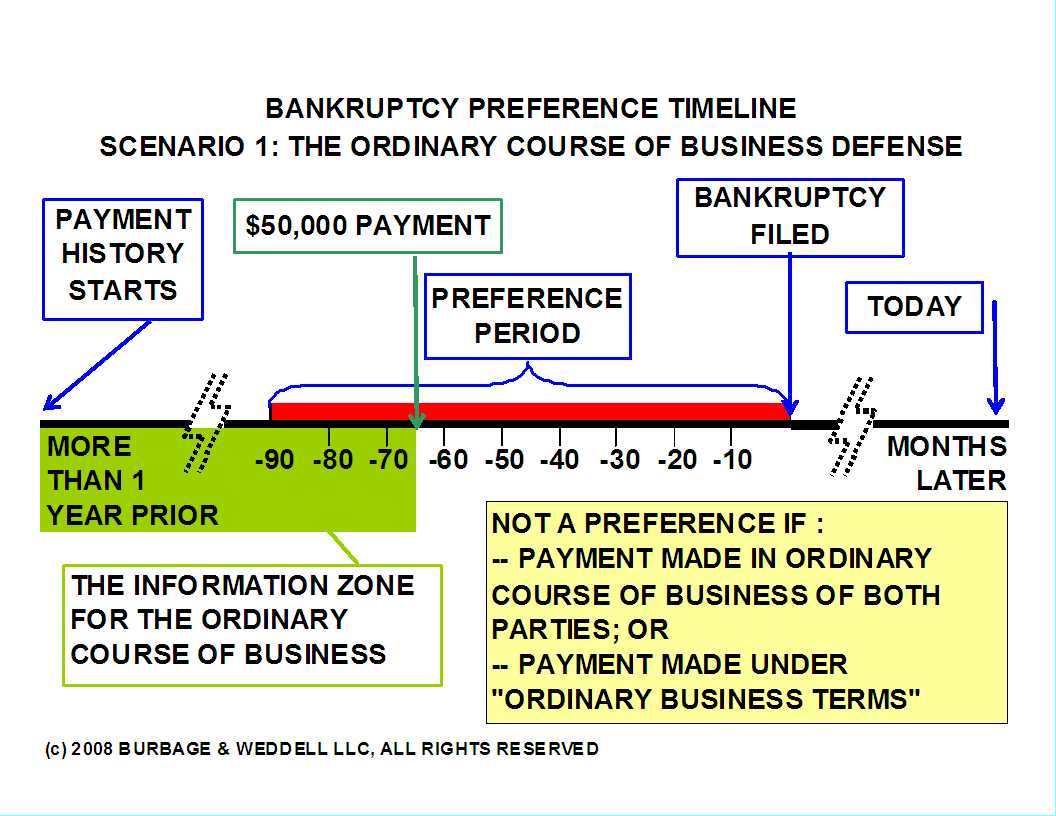
Assessing and Proving the Ordinary Course of Business Defense to a
PPT Innovation, Technology, and Ordinary Course of Business
Related Party Transactions ppt download
Ordinary Course Of Business Is A Legal Term That Has Its Roots In The Uniform Commercial Code (Ucc) As It Pertains To Commercial Transactions.
The Usual Transactions, Customs And.
When A Party Seeks To Recover Costs Or Damages From A Transaction That Was Made Impossible By A Breach Or Tort, The Courts Use Ordinary Course Of Business Calculations To Ascertain How.
It Is Often Necessary For The Bankruptcy Courts To Determine Whether Certain Conduct Is In The Ordinary Course Of Business. This Issue May Arise In Several Dif Ferent Contexts.
Related Post: